‘Serious Games’, videogames for educational purposes, are gaining popularity in basic education, entrepreneurship education and therapy. A report of the Complutense University of Madrid, informs Tendencias 21, explains that this kind of games are designed for maintaining the level of challenge and the attention of the player, and make education different since they are not based on memorising, but on learning and applying knowledge in a safe environment where failure is acceptable.
The report, ordered by the Computer Engineering Director and Deans Council (CODDII) to professors of the Complutense University, explains that the design principles of videogames make them suitable for education: they are designed for maintaining the level of challenge and the attention of the player. Moreover, these videogames make education different since they are not based on memorising, but on learning and applying knowledge in a safe environment where failure is acceptable.
What started out in the 80s as an isolated idea has become a line of work with a high turnover rate, with growth rates even higher than the ones of the global industry of videogames, and an institutional support as emerging technology.
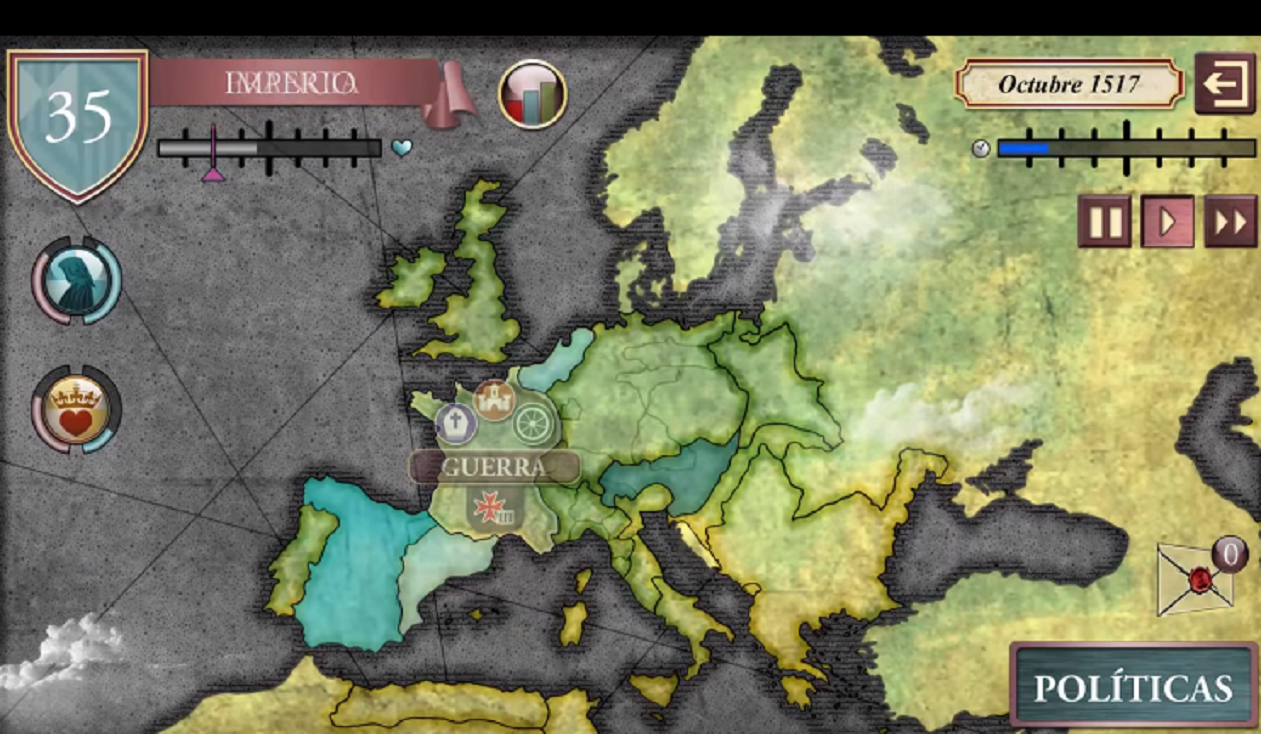
The term ‘Serious Games’ may apply to all games and simulations for any purpose other than entertainment. For example, ‘Carlos, Rey Emperador’ (linked to the namesake television series of RTVE), apart from having entertainment game mechanisms, has two additional functions: preserving the interest for the events of the series and experimenting and learning the History of Spain in an alternative way.
Serious videogames focused on teaching can be used as a complement or as an alternative way for acquiring knowledge from a formal educational programme, in subjects such as Mathematics, Ethics, Knowledge Environment or languages.
There are also serious games for working purposes: for training heavy equipment workers or laboratory technicians, or flight simulators. Many armies used these serious games for training their soldiers.
Games oriented to troubleshooting are used for developing decision making abilities in business environments or as multicultural training for conflict resolution.
There are also serious games oriented to therapy, where the objective is to modify the behavior of the players or their relationships, treat dyslexia, overcome a phobia or battle against a disease, as for example cancer, with games such as Mission.
The report, ordered by the Computer Engineering Director and Deans Council (CODDII) to professors of the Complutense University, explains that the design principles of videogames make them suitable for education: they are designed for maintaining the level of challenge and the attention of the player. Moreover, these videogames make education different since they are not based on memorising, but on learning and applying knowledge in a safe environment where failure is acceptable.
What started out in the 80s as an isolated idea has become a line of work with a high turnover rate, with growth rates even higher than the ones of the global industry of videogames, and an institutional support as emerging technology.
The term ‘Serious Games’ may apply to all games and simulations for any purpose other than entertainment. For example, ‘Carlos, Rey Emperador’ (linked to the namesake television series of RTVE), apart from having entertainment game mechanisms, has two additional functions: preserving the interest for the events of the series and experimenting and learning the History of Spain in an alternative way.
Serious videogames focused on teaching can be used as a complement or as an alternative way for acquiring knowledge from a formal educational programme, in subjects such as Mathematics, Ethics, Knowledge Environment or languages.
There are also serious games for working purposes: for training heavy equipment workers or laboratory technicians, or flight simulators. Many armies used these serious games for training their soldiers.
Games oriented to troubleshooting are used for developing decision making abilities in business environments or as multicultural training for conflict resolution.
There are also serious games oriented to therapy, where the objective is to modify the behavior of the players or their relationships, treat dyslexia, overcome a phobia or battle against a disease, as for example cancer, with games such as Mission.

 English
English



